High Blood Sugar
According to a 2022 post by the Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), over 11% of ALL people in the United States have high blood sugar – that equates to a little over 37 million people. Further, they have concluded that ~38% of adults in the US (over 96 million people) have PRE-diabetes… 96 MILLION PEOPLE! Those statistics don’t even include the many young men and women (younger than 18) that also have high blood sugar.
Blood sugar can become high due to 3 main scenarios — (1) Type 1 diabetes, (2) Type 2 diabetes/Insulin Resistance, or (3) Gestational diabetes. Type 1 diabetes occurs when your immune system has an autoimmune reaction to your beta-cells in the pancreas – the cells responsible for producing insulin. Type 2 diabetes is caused by severe insulin resistance (your pancreas produces enough insulin but your cells become resistant to it). Gestational diabetes is a high blood sugar problem that only occurs in females during pregnancy.
Since type 2 diabetes makes up the overwhelming majority of high blood sugar cases, we will focus on the driver of this deadly disease: Insulin resistance.
What Is Insulin Resistance?
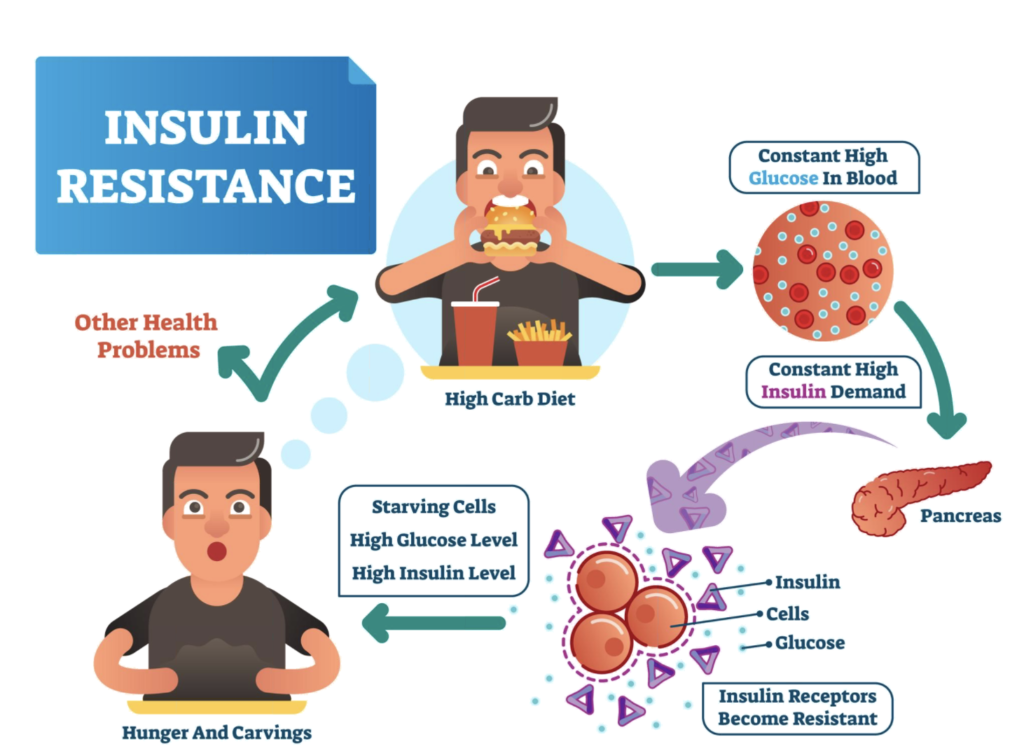
Insulin resistance is when cells become resistant to insulin. Cells become resistant to insulin anytime there is an imbalance between the amount of glucose in the blood and the cells’ ability to handle it. This can happen via 2 different mechanisms: (1) simply having too much glucose or (2) the cells are unable to properly handle what may otherwise be normal amounts of glucose. In either scenario, glucose steadily increases in the blood resulting in increased insulin released from the pancreas. In response, our cells down-regulate (decrease) the insulin receptors from their cell membrane as a protective mechanism. If the cells let in too much glucose, the cells would undergo too much oxidative damage from glycolysis and die.
If insulin resistance becomes severe enough, it becomes Type 2 Diabetes. While this can still be reversed naturally, the sooner you can begin the process of reversing it, the better. In cases of advanced insulin resistance (Type 2 diabetes) and mild cases, many people experience the following signs and symptoms.
Signs and Symptoms of Insulin Resistance
- Fatigue (tiredness) – especially after you eat
- Must have sweets after meals
- Difficulty losing weight
- Crave sweets – even after eating sweets
- Increased appetite
- Increased belly fat (larger than your hip girth)
- Increased fat on the back of your arms
- Hormonal imbalances
The 4 Main Causes For Insulin Resistance
Any and all of these things should be addressed for optimal health and optimal blood sugar regulation.
1) Carbohydrate and Protein Relationship
Carbs, carbs, carbs — that is what is on most people’s plate today. Between the cereal/pancakes/waffles/juice for breakfast, the sandwich/chips/soda for lunch, and the pasta/pizza/breads/desserts for dinner, American’s have been drenched in a diet consisting of carbohydrates. All of these carbohydrates will overwhelm our body’s ability to handle the glucose well. Along with this, most people aren’t eating enough protein. Insulin resistance can occur because of an imbalance between too many carbohydrates and/or not getting enough protein. The liver’s main source of fuel for handling glucose is protein. We must make protein a priority to reverse insulin resistance!
2) Inflammation
Inflammation is a large contributor to insulin resistance as it interferes with cells’ overall functioning , including their ability to handle insulin. While the topic of inflammation is a large one, many sources consist of physical stress, chemical chemical, internally produced toxicities, subclinical infections, emotional stress, and radiation exposure. Physical stress includes the fascial system, injuries, traumas, large amounts of physical demand. Chemical stress includes stress hormones, poor lymph flow, heavy metals, plastics, GMOs, pesticides/fertilizers, and more. Internally produced toxicities and subclinical infections are explained further below. Emotional stress includes trauma, trapped emotions, and more. Radiation exposure includes 5G towers, wifi routers, our cell phones, etc.
3) Toxicities
Toxicities can come from a number of places (this list is not exhaustive): (1) from the outside world such as heavy metals, plastics/xeno-estrogens, aldehydes (inhaled mold spores), GMO foods, pesticides/fertilizers; (2) from inside our body such as ammonia (from infections), aldehydes (from infections), homocysteine (from poor methylation), medications, and hormones (estrogen, stress hormones, etc.); and (3) from the power of our words and thoughts.
4) Subclinical Infections
Many people struggle with subclinical infections but few even know about them or what they are. Subclinical infections simply mean you have an infection but you may not have a fever, chills and sweats, burning or pain, coughing, a runny nose, or be contagious. Rather, you may have parasites, viruses, bacterial overgrowth, or fungal overgrowth causing dysfunction in your body. Infections will deplete you of your nutrients, leave behind their metabolic wastes, and contribute to a variety of health problems. Signs and symptoms of infections include changes in energy, mental focus, inflammation, blood sugar regulation, hormonal imbalances, sleep quality, digestive health, thyroid function, and so much more. This topic is likely the most unexplored topic by the average physician today, yet arguably the most important for overall health and function. This is a short explanation of subclinical infections — a whole article on the topic can be found here.
Overcoming Insulin Resistance Naturally
These are the next recommended steps to consider: lifestyle changes, nutritional support, and professional recommendations if necessary.
- Nutritional support: eating too many carbs and not enough protein? Focus on decreasing overall carbohydrate intake (~0-10g/meal) and focus on 20-40g of protein per meal. Avoid snacking unless it is a good protein or fat source and absolutely necessary. As always, the quality sources of your food is going to essential – I explain all of that in this article HERE.
- Intermittent fasting: Intermittent fasting should be done from ~4pm through the night and into the morning to support liver autophagy (self-cleansing). Eating between an 8-hour window is generally recommended but you can always make that window smaller for increased benefits. If you are going to do intermittent fasting the right way, you want to focus on your eating window starting with breakfast – from 8am-4pm with a heavy protein breakfast. This will allow your body to optimally regulate your stress hormones (which are naturally highest in the mornings) throughout the rest of the day.
- Interval training: focus on interchanging slow aerobic/low intensity activity such as walking with an intense activity such as jogging or running. For example, walk for ~4 minutes, followed by jogging or running for ~2 minutes, and so on. By doing this type of workout approach, you will train your body to utilize the glucose in the blood and thus improve insulin resistance.
Struggling With High Blood Sugar or Type 2 Diabetes?
At Freedom Health and Wellness, we address all of these things and more through a personalized and functional approach. We help people with chronic diseases and illnesses regain their health by getting to the source of their health concerns.
Have Questions?
Dr. Miller offers a free zero-risk 15-minute consult to address any questions or concerns prior to committing to care! Just click the button below to schedule your free consult and get to spend 15-minutes with Dr. Miller
Schedule Today!
If you are looking for a doctor who is genuine, compassionate, and most importantly, able to help you, click below to schedule your first appointment. We are excited to see life-changing results with you!